How MindFlight Orchestrator (MFO) Works: A Detailed Walkthrough¶
flowchart LR
subgraph External Event Sources
Chatbot((Chatbot))
Webhook((Webhook))
SaaS((SaaS))
end
subgraph MFO Client - Local Orchestrator
EventReceiver --> WorkflowLoader
WorkflowLoader --> StateManager
StateManager --> TaskExecutor
TaskExecutor --> StateManager
end
subgraph MFO Server - Stateless API Provider
ResourceAPI[/"Resource API"/]
LLMAPI[/"LLM API"/]
ToolAPI[/"Tool API"/]
MemoryAPI[/"Memory API"/]
end
WorkflowYAML[(Workflow YAML)]
Chatbot <--> EventReceiver
Webhook --> EventReceiver
SaaS <--> EventReceiver
WorkflowLoader --> WorkflowYAML
TaskExecutor --> ResourceAPI
TaskExecutor --> LLMAPI
TaskExecutor --> ToolAPI
TaskExecutor --> MemoryAPI
ResourceAPI --> TaskExecutor
LLMAPI --> TaskExecutor
ToolAPI --> TaskExecutor
MemoryAPI --> TaskExecutor1. Event-Driven, Client-Orchestrated Automation¶
- External Event Occurs: A customer submits a feedback form (or any other business event happens ; chatbot, webhook, internal application ...).
- MFO Client Captures the Event: The MFO Client receives the event and loads the relevant workflow.
- MFO Client Orchestrates the Workflow:
- The client matches the event to a trigger and launches the corresponding taskflow.
- All workflow logic, state, and step execution is managed locally in the client.
- For each task in the workflow:
- The client makes a remote API call to the MFO server (for LLM, resource, tool, memory, etc.).
- The client processes the response, updates local state, and determines the next step.
- Some tasks (like
ask_user) may require local user interaction.
- Workflow Execution Example:
| Step | Action | Behind the scene |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: | Store the feedback | Client calls MFO server resource API. |
| Step 2: | Analyze sentiment with AI | Client calls MFO server LLM API. |
| Step 3: | Tag feedback as Positive/Negative | Client calls MFO server tool API. |
| Step 4: | Notify the customer support team on Slack | Client calls MFO server tool API. |
- Outcome: The feedback is categorized, logged, and actioned automatically—all orchestration and state management happens in the client.
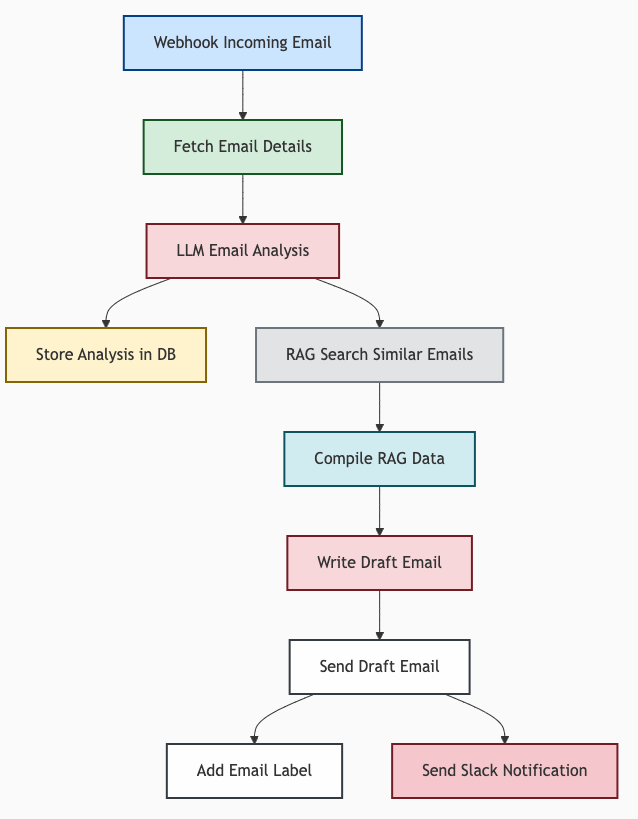
2. Extended Example: Intelligent Email Processing¶
Scenario: A new customer email arrives in support. The MFO client:
| Action | Behind the scene |
|---|---|
| Fetches its content | (calls MFO server resource API). |
| Uses AI to summarize it | (calls MFO server LLM API). |
| Stores the summary | (calls MFO server memory API). |
| Labels the email's priority in the inbox | (calls MFO server tool API). |
Workflow YAML (Simplified):
- id: "get_email_content"
type: "mfo_api_resource_get"
config:
resource_id: "${INPUT.resource_id}"
- id: "analyze_email"
type: "mfo_api_chat_send"
config:
prompt_template_id: "summarize_email"
prompt_context:
email_content: "get_email_content.resource.content"
provider_id: "openai"
dependencies: ["get_email_content"]
- id: "store_summary"
type: "mfo_api_memory_store"
config:
key: "email_summary_${INPUT.resource_id}"
value: "analyze_email.parsed_content.summary"
dependencies: ["analyze_email"]
- id: "tag_email"
type: "mfo_api_tool_execute"
config:
tool_id: "email.tag_thread"
arguments:
thread_id: "${INPUT.thread_id}"
tag: "AI_Summarized"
dependencies: ["store_summary"]
3. Why YAML? Visual, Accessible, and Collaborative¶
- YAML workflows are readable as process diagrams.
- Accessible to all stakeholders:
- Business users, IT, operations, marketing, and support can all read and contribute.
- AI-powered assistance:
- The MFO platform includes an AI agent that can answer questions, help write/modify workflows, and explain logic in natural language.
4. Visualizing Workflows¶
- Mermaid diagrams and other tools can be generated from YAML for visual process mapping.
5. Collaboration & Agility¶
- Direct involvement: All company stakeholders can help build and evolve workflows.
- Agile process evolution: Business and technical teams collaborate seamlessly.
6. Use Cases and Business Relevance¶
Readability & Accessibility¶
- MFO's YAML format is designed for clarity.
- All stakeholders can participate in workflow design and review.
Service Eligibility¶
- Any service with a REST API can be automated via MFO.
- This includes SaaS tools (Salesforce, HubSpot, SAP, etc.) and custom internal systems.
- Rapid integration of MCP server modules (model context protocol)
- Creation of MFO providers based on OpenAPI documentation
Multi-Departmental Structuring¶
- Multiple MFO servers can be deployed for different departments (support, marketing, finance, etc.).
- This allows for compartmentalization, vendor separation, and strict security controls.
Scalability & Complexity¶
- No hard limits:
- Workflows can be modular, with sub-workflows and reusable components.
- The only constraint is the capacity of the chosen AI models for certain tasks.
Connectors & Integration¶
- Providers are defined using OpenAPI specs for each tool.
- MFO can integrate with any tool that exposes a standard API.
- For tools without OpenAPI, a custom provider can be created.
7. Key Architectural Principles¶
- Client-Orchestrated: All workflow logic, state, and step execution is managed by the MFO client.
- Server as Provider: The MFO server exposes APIs for LLM, memory, resources, and tools, but does not manage workflow state or orchestration.
- Stateless Server: The server is stateless with respect to workflow orchestration; all state is managed by the client.
- Extensible & Modular: New providers and tools can be added to the server without changing client logic.
- Secure & Auditable: All sensitive operations are authenticated and logged.
In summary: MFO enables organizations to automate, orchestrate, and evolve business processes with clarity, security, and agility—using readable YAML, AI-powered assistance, and robust integration with any API-driven service.
All orchestration and state management happens in the client; the server is a powerful, extensible provider of business capabilities.