At its core, every business runs on events (a customer inquiry, a payment received, a contract signed) and responses (notify sales, update records, trigger support). If these flows are fragmented, decisions slow down, costs rise, and customer experience suffers. If they are orchestrated seamlessly, the organization moves faster, smarter, and with fewer errors. That is the essence: connect events to outcomes in the simplest possible way.
Now, let’s place this into context with a clear storyline.
Situation
Companies today rely on dozens of SaaS platforms, CRMs, analytics tools, and communication channels. Each solves a problem, but together they create a jungle of processes that employees must navigate manually.
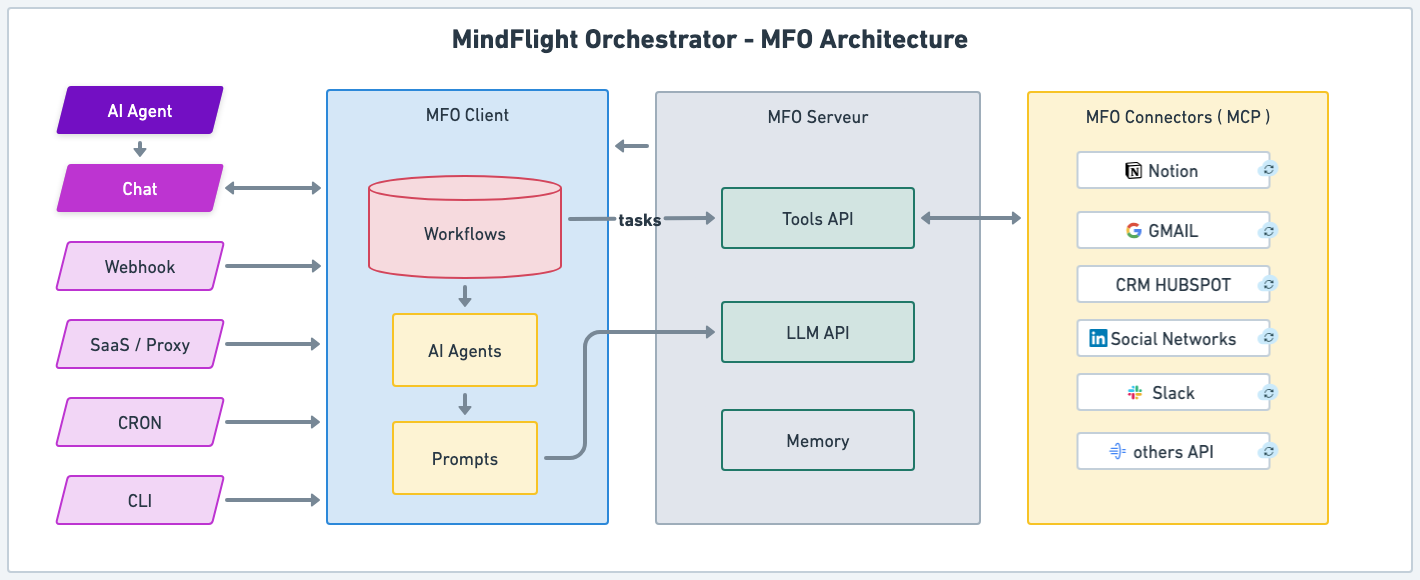
How MFO works - let's find out
Complication
This fragmentation leads to delays, inconsistent data, and missed opportunities. IT teams are overwhelmed with integration projects, while business teams feel the gap between strategic goals and daily execution.
Question
How can leaders ensure that every customer touchpoint or business event automatically triggers the right next step—without locking themselves into heavy, inflexible IT projects?
Answer
This is where MindFlight Orchestrator (MFO) comes in.
Think of MFO as a conductor for your digital orchestra. The intelligence—the score, the rhythm, the flow—lives in the client, close to your team. The server provides the instruments: AI models, APIs, tools, and memory. The result is a system where:
Workflows remain transparent and editable in plain YAML, understandable by both business and technical stakeholders.
Execution is agile and secure because orchestration and state are managed locally, not locked into a central black box.
Integration scales effortlessly since any service with an API can be plugged in as a new instrument in the orchestra.
The impact for executives is straightforward:
- Faster response times and fewer errors in customer-facing processes.
- Lower IT dependency for everyday automation.
- Stronger governance and compartmentalization across departments.
In short, MFO transforms the way organizations connect strategy to execution: with clarity, agility, and control.
What else should you know?
That all the technical details, diagrams, and workflow examples you’ll see below simply illustrate this core idea: events become orchestrated outcomes, and the orchestra is always in your hands.
1. Event-Driven, Client-Orchestrated Automation
- External Event Occurs:
A customer submits a feedback form (or any other business event happens ; chatbot, webhook, internal application ...). - MFO Client Captures the Event:
The MFO Client receives the event and loads the relevant workflow. - MFO Client Orchestrates the Workflow:
- The client matches the event to a trigger and launches the corresponding taskflow.
- All workflow logic, state, and step execution is managed locally in the client.
- For each task in the workflow:
- The client makes a remote API call to the MFO server (for LLM, resource, tool, memory, etc.).
- The client processes the response, updates local state, and determines the next step.
- Some tasks (like
ask_user) may require local user interaction.
- Workflow Execution Example:
| Step | Action | Behind the scene |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: | Store the feedback | Client calls MFO server resource API. |
| Step 2: | Analyze sentiment with AI | Client calls MFO server LLM API. |
| Step 3: | Tag feedback as Positive/Negative | Client calls MFO server tool API. |
| Step 4: | Notify the customer support team on Slack | Client calls MFO server tool API. |
- Outcome:
The feedback is categorized, logged, and actioned automatically—all orchestration and state management happens in the client.
2. Extended Example: Intelligent Email Processing
Scenario:
A new customer email arrives in support. The MFO client:
| Action | Behind the scene |
|---|---|
| Fetches its content | (calls MFO server resource API). |
| Uses AI to summarize it | (calls MFO server LLM API). |
| Stores the summary | (calls MFO server memory API). |
| Labels the email's priority in the inbox | (calls MFO server tool API). |
Workflow YAML (Simplified View):
- id: "get_email_content"
type: "mfo_api_resource_get"
config:
resource_id: "${INPUT.resource_id}"
- id: "analyze_email"
type: "mfo_api_chat_send"
config:
prompt_template_id: "summarize_email"
prompt_context:
email_content: "get_email_content.resource.content"
provider_id: "openai"
dependencies: ["get_email_content"]
- id: "store_summary"
type: "mfo_api_memory_store"
config:
key: "email_summary_${INPUT.resource_id}"
value: "analyze_email.parsed_content.summary"
dependencies: ["analyze_email"]
- id: "tag_email"
type: "mfo_api_tool_execute"
config:
tool_id: "email.tag_thread"
arguments:
thread_id: "${INPUT.thread_id}"
tag: "AI_Summarized"
dependencies: ["store_summary"]
Explanation:
- The MFO client loads this YAML, manages all dependencies, and executes each step in order.
- Each step is a remote call to the MFO server, but the orchestration, state, and error handling are all local to the client.
3. Why YAML? Visual, Accessible, and Collaborative
- YAML workflows are readable as process diagrams.
- Accessible to all stakeholders:
- Business users, IT, operations, marketing, and support can all read and contribute.
- AI-powered assistance:
- The MFO platform includes an AI agent that can answer questions, help write/modify workflows, and explain logic in natural language.
4. Visualizing Workflows
- Mermaid diagrams and other tools can be generated from YAML for visual process mapping.
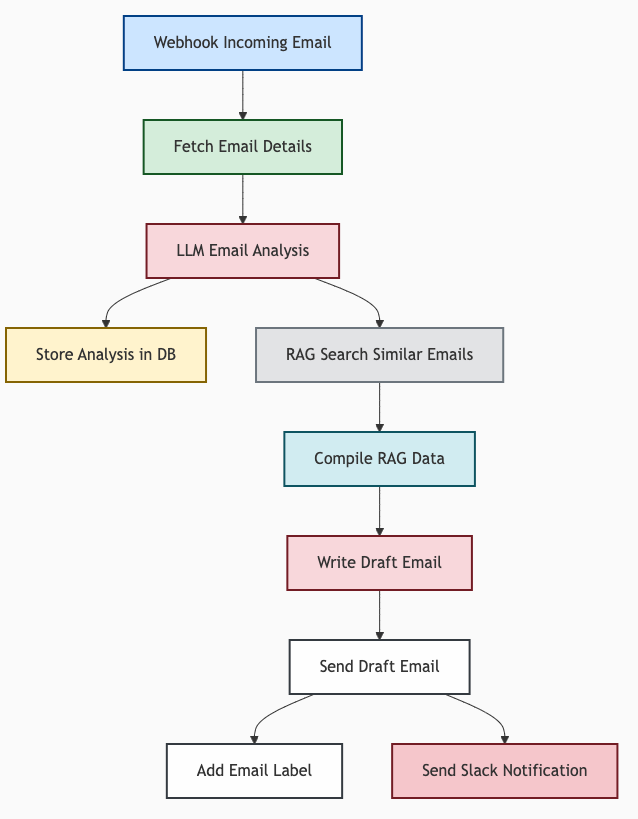
5. Collaboration & Agility
- Direct involvement:
All company stakeholders can help build and evolve workflows. - Agile process evolution:
Business and technical teams collaborate seamlessly.
6. Use Cases and Business Relevance
Readability & Accessibility
- MFO's YAML format is designed for clarity.
- All stakeholders can participate in workflow design and review.
Service Eligibility
- Any service with a REST API can be automated via MFO.
- This includes SaaS tools (Salesforce, HubSpot, SAP, etc.) and custom internal systems.
- Rapid integration of MCP server modules (model context protocol)
- Creation of MFO providers based on OpenAPI documentation
Multi-Departmental Structuring
- Multiple MFO servers can be deployed for different departments (support, marketing, finance, etc.).
- This allows for compartmentalization, vendor separation, and strict security controls.
Scalability & Complexity
- No hard limits:
- Workflows can be modular, with sub-workflows and reusable components.
- The only constraint is the capacity of the chosen AI models for certain tasks.
Connectors & Integration
- Providers are defined using OpenAPI specs for each tool.
- MFO can integrate with any tool that exposes a standard API.
- For tools without OpenAPI, a custom provider can be created.
7. Key Architectural Principles
- Client-Orchestrated:
All workflow logic, state, and step execution is managed by the MFO client. - Server as Provider:
The MFO server exposes APIs for LLM, memory, resources, and tools, but does not manage workflow state or orchestration. - Stateless Server:
The server is stateless with respect to workflow orchestration; all state is managed by the client. - Extensible & Modular:
New providers and tools can be added to the server without changing client logic. - Secure & Auditable:
All sensitive operations are authenticated and logged.
In summary:
MFO enables organizations to automate, orchestrate, and evolve business processes with clarity, security, and agility—using readable YAML, AI-powered assistance, and robust integration with any API-driven service.
All orchestration and state management happens in the client; the server is a powerful, extensible provider of business capabilities.